Hello again! It has been a while since my last post. Previously, I shared how I knew I wanted to work as a freelance web designer and my interest in user experience design a.k.a UX design. Since then, I have been reading up a lot on it, watching YouTube videos and signing up for online courses. I thought it would be a great learning process to also document what I have learnt so far.
If you are interested in UX design as well, then continue reading to gain some insight! Feel free to point out my mistakes if you see any! I hope this can become a platform for everyone to contribute and learn too.
What is User Experience (UX)?
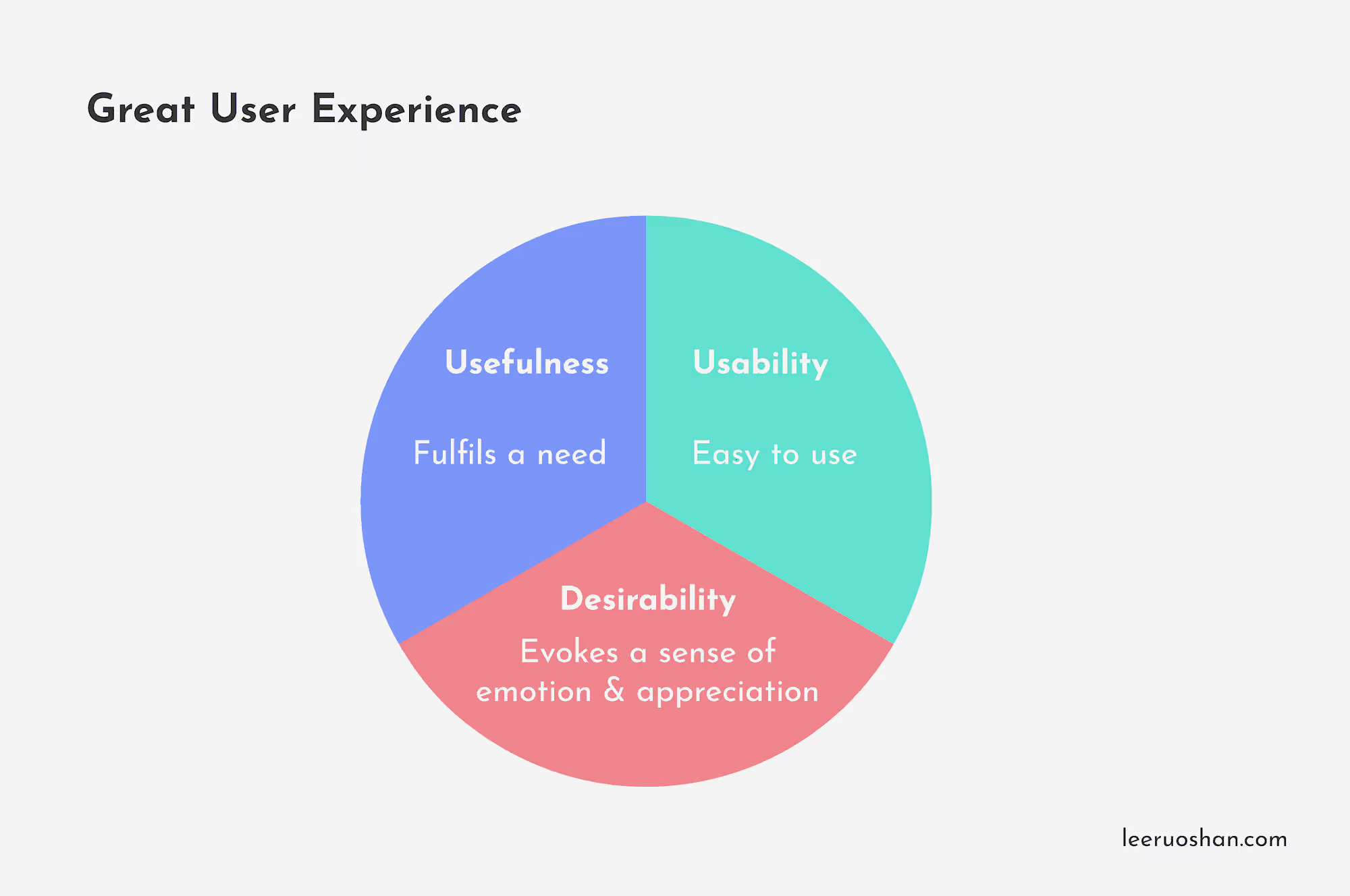
UX is the overall experience a user has when he interacts with a company, its products or services. UX is not limited to the digital domain, it can be applied in any industry. A great user experience comprises of 3 key factors namely: usability, desirability and usefulness. It determines whether a product or service has a good or bad UX.
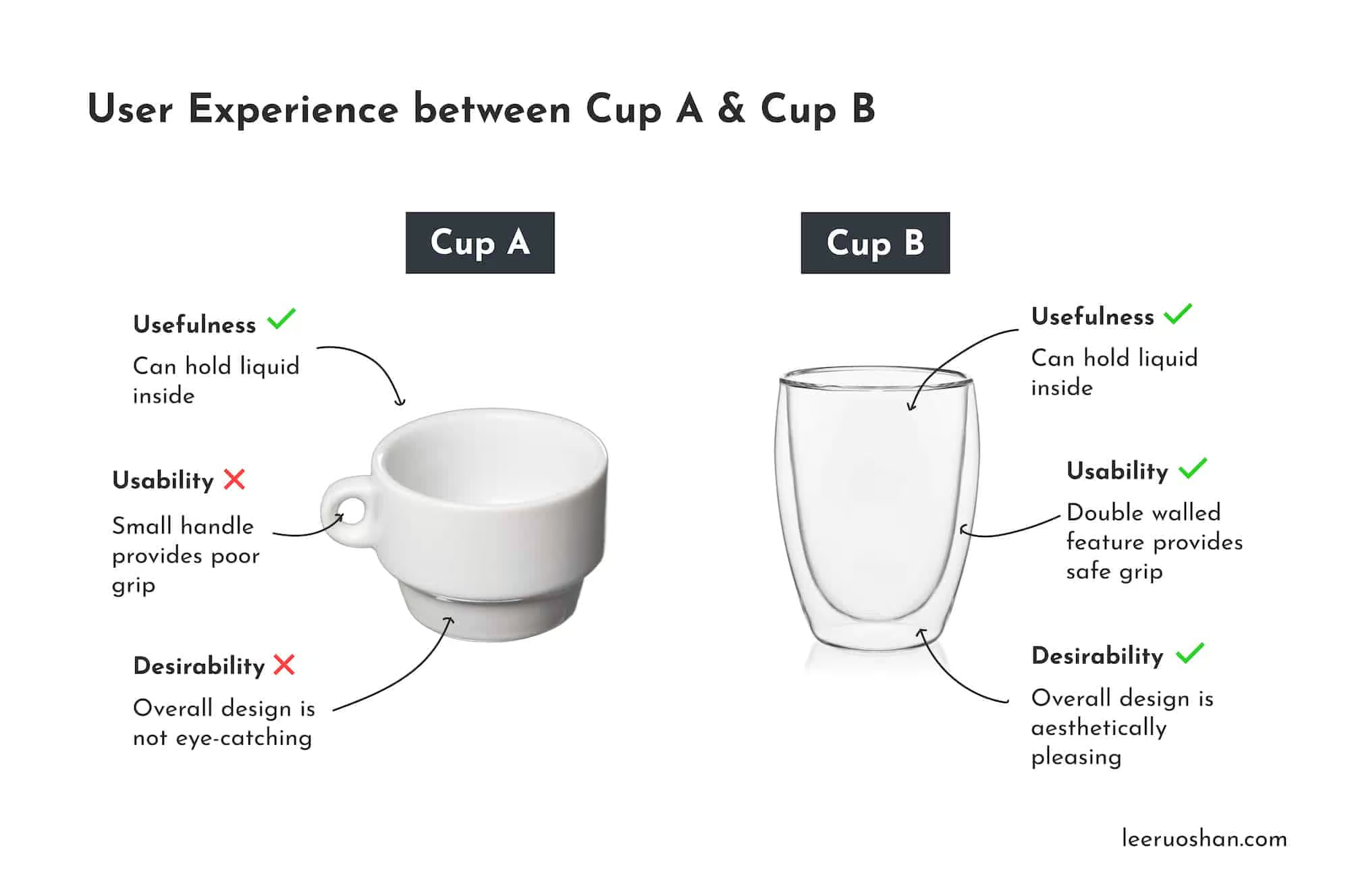
We can explain a user’s experience when using 2 different types of cup. Look at Cup A. Cup A fulfils a need as it can hold water in it. However, if we take a closer look at its handle, you will notice that its a little small for one to hold onto it comfortably. Without a proper and comfortable grip, one can easily spill their drinks.
Now look at Cup B. It fulfils a need just like Cup A. Though it does not have a handle on the side, its double walled feature provides a proper and safe grip. When the content inside is cold, the double walled feature prevents condensation from happening on the outside of the cup. When the content inside is hot, it keeps the outside of the cup safe to be handled.
In terms of desirability… we can all agree Cup B is the more aesthetically pleasing out of the 2. As such, we say Cup A has a bad UX and Cup B has a good UX.
UX can be applied on almost everything. Look around you and try applying these 3 key factors on things to see if its good or bad UX!
User Experience (UX) Design
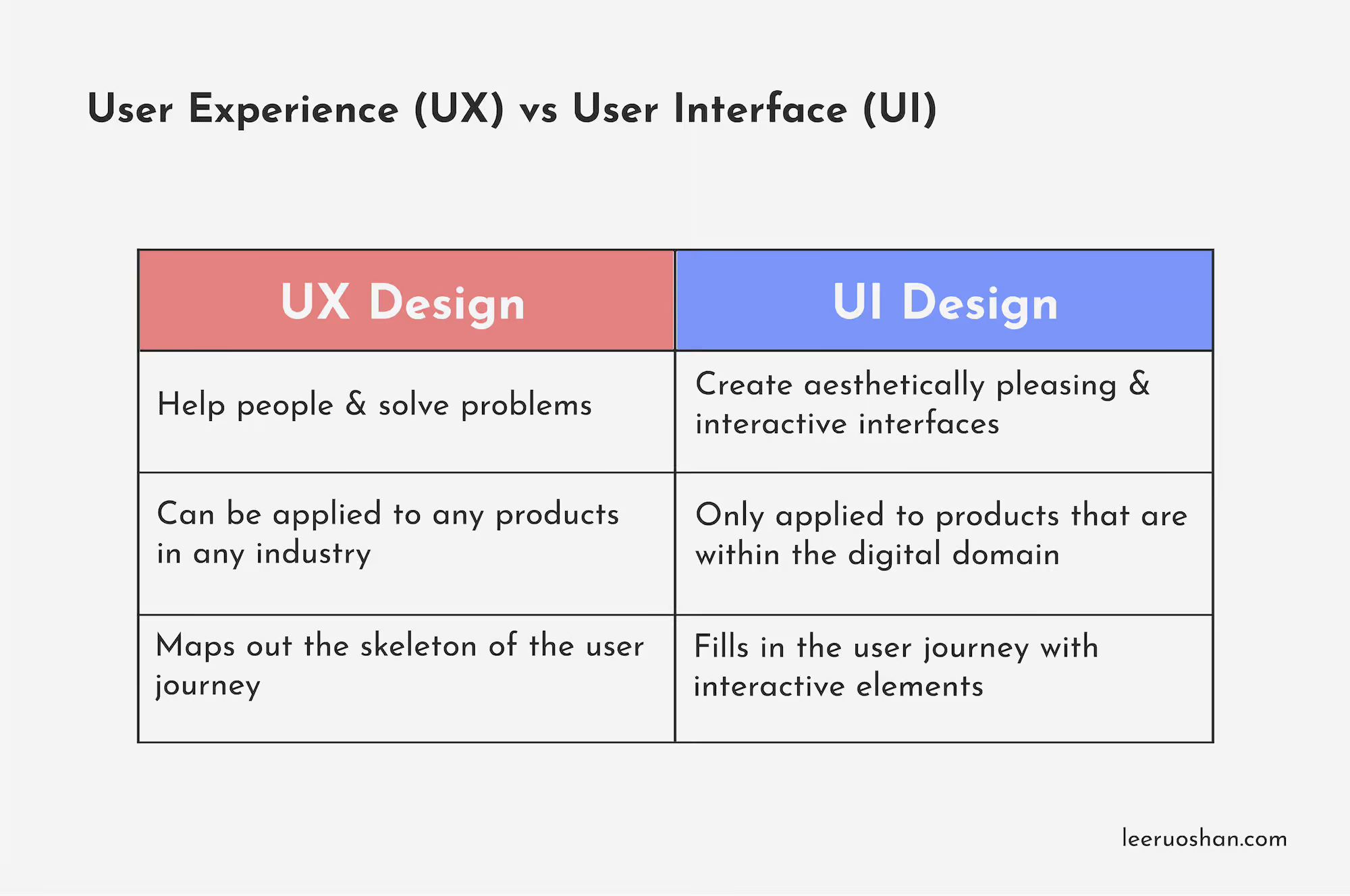
UX design is building products specifically to the needs of users. Going back to the comparison on Cup A and B, we can say that Cup B is the better designed out of the 2. Essentially, UX design is all about helping users and solving and their problems!
User Experience (UX) Design vs User Interface (UI) Design
You probably would have heard of UI design too. Unlike UX design, UI design takes place almost entirely within the digital domain. It deals with the visual aspect of a screen-based action a user takes on the app on his phone or even pages of a website. UI is concerned with the overall look and feel of a design, and is a crucial aspect of user experience. UX design usually comes first in the development process, followed by UI design.
User Experience (UX) Design Process
Now that you know what UX is, and the difference between UX and UI, let’s move on to the process of UX design. It is important to keep your users in mind in all steps of creating a product or service. We call this “user-centred design”. An end product is not considered to have good UX if it does not address the needs of your users.
Disclaimer: The following information are what I have learnt and gathered from various courses that I have gone through such as FutureLearn and Career Foundary.
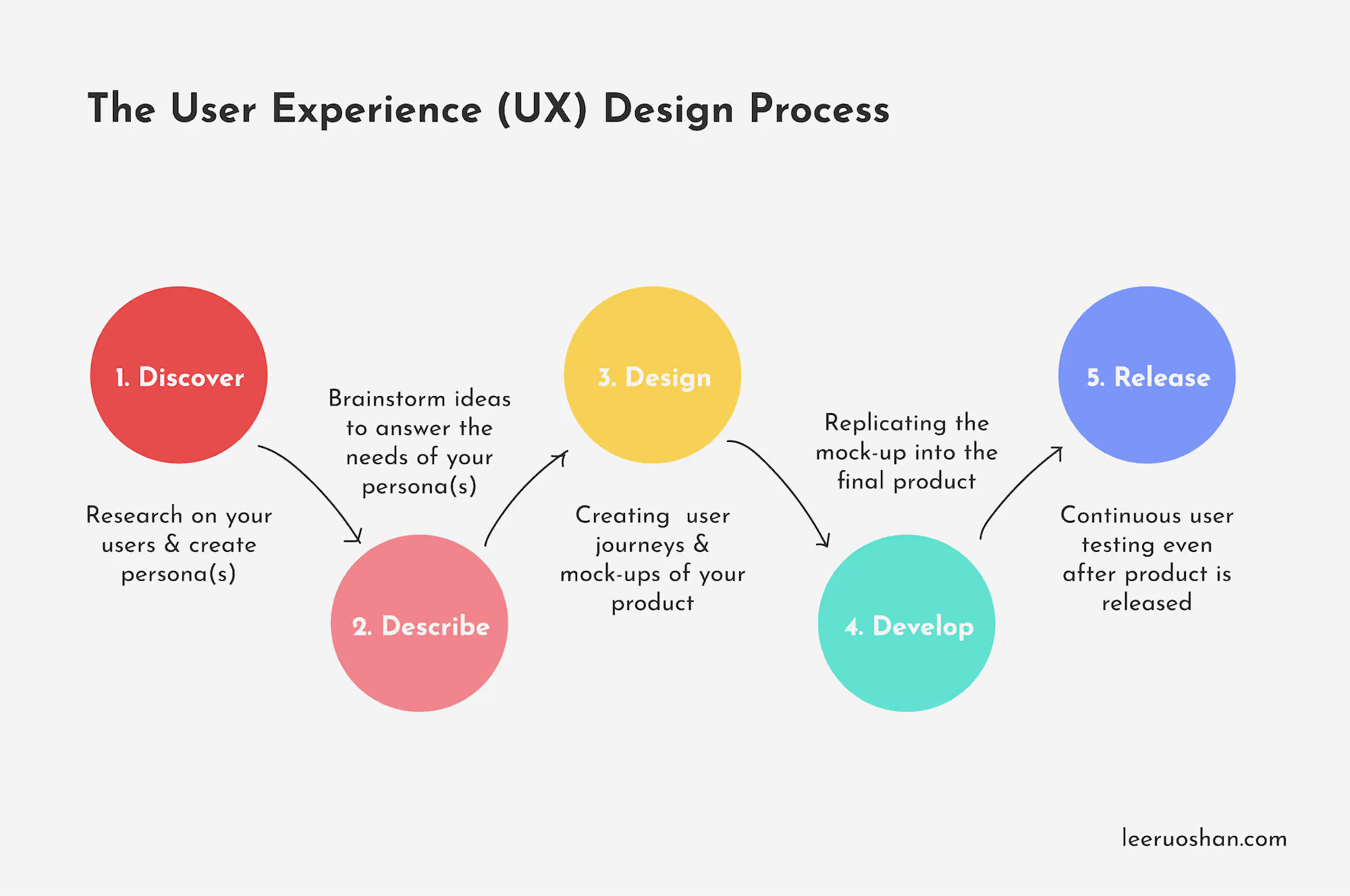
The UX design process consists of 5 steps: Discover, Describe, Design, Develop and Release.
Step 1: Discover
As with all projects or assignments, you usually begin with a research. The same goes for the UX design process.
Research
At this stage, you have to understand what your users need, their pain points, how they think and how they behave. The best way to understand your users is by getting inputs from real users. There are many ways to learn about your users.
Focus groups and interviews are great head start to the research process. These people could be the public, your co-workers, friends or family depending on your project. You can also create surveys to be sent out to the mass public.
With all the research, you are going to get many valuable responses that can be used to draw commonalities or differences amongst different groups of users.
Affinity mapping is the process of grouping quotes or observations into one cluster to draw meaningful insights. These insights will help you define the problem(s) and develop potential ideas for solutions.
You should also conduct market and competitor research to see what is out there.
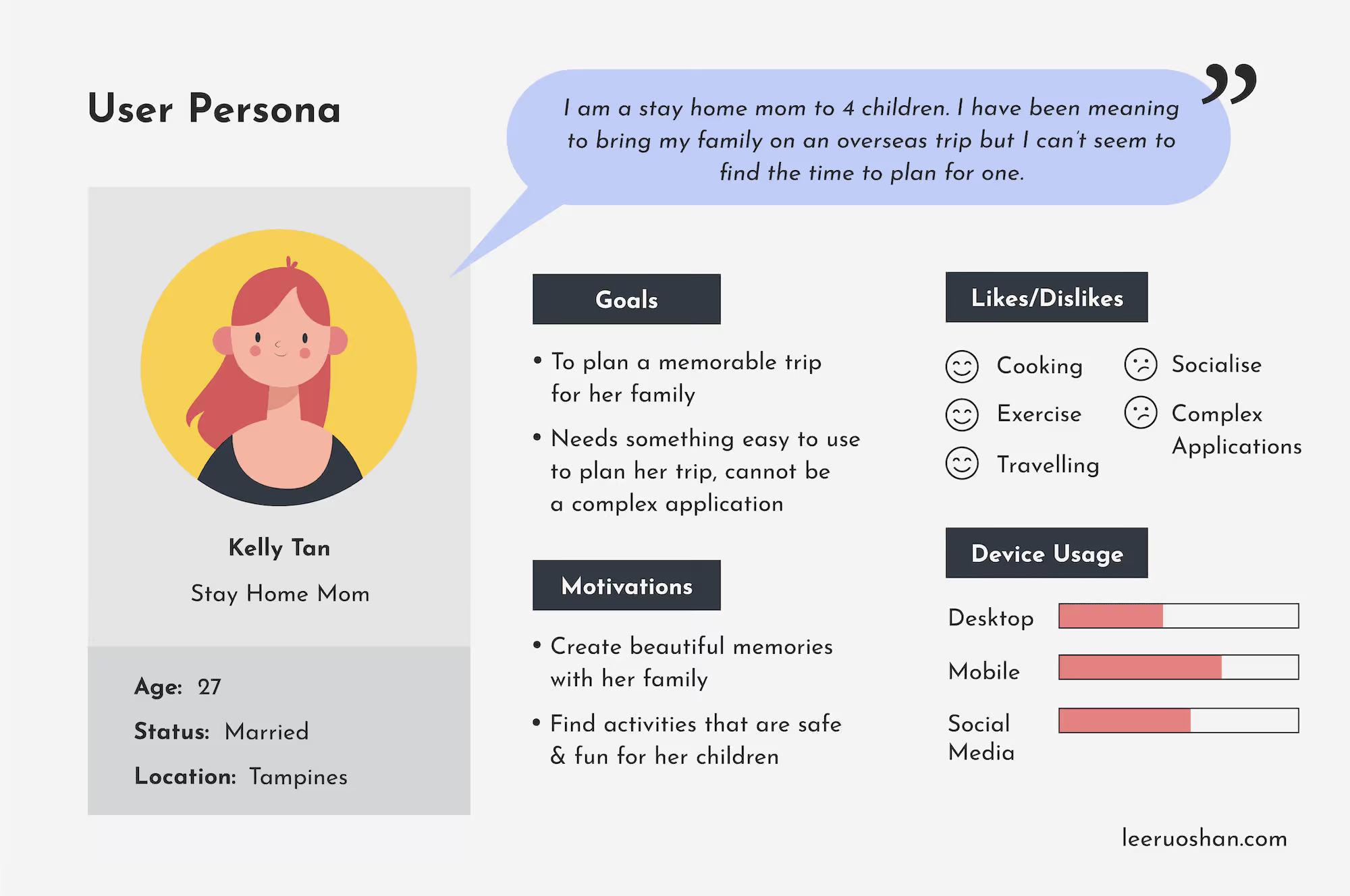
Create a User Persona
From the insights through your research, you will want to create a user persona. Again, you can have more than one persona depending on your project. User personas are fictional but realistic representations of a target user based on the goals, needs and pain points derived from your research. They help to humanize the different target groups so UX designers can build empathy with them throughout the entire UX design process.
Here are some tips when creating a user persona:
- Start with a short story about who the person is
- What are the goals and motivation of this user?
- What is the user’s likes and dislikes?
- Include a back story of how the user is using an existing product or service
Step 2: Describe
After creating a user persona based on your research, you would likely have an idea of what you want your product or service to do. List them down!
Brainstorming
The goal of brainstorming is to throw in all possible ideas under the sun that will also answer the problems and needs of your user persona. At this stage, you have to keep in mind the motivations and goals of your user persona.
They will guide you in the brainstorming of ideas and solutions. It is also very helpful to use sticky notes and a whiteboard to create a mind-map with your ideas. You can see how one idea leads to another and how they eventually lead to a solution.
Define Your Requirements
With brainstorming, you are going to come up with ideas that may not be actually feasible for your project. This is where you need to be more specific, narrowing down and define what is most important for your solution.
Essentially, you have to sieve through the ideas you have brainstormed and pick out those that are critical to your solution and feasible with whatever you have limited yourself to e.g. your project budget. What is left after sieving through your brainstormed ideas will most likely be a mix of what is feasible and within your needs.
Step 3: Design
Now comes the part where most people are looking forward to, the design stage!
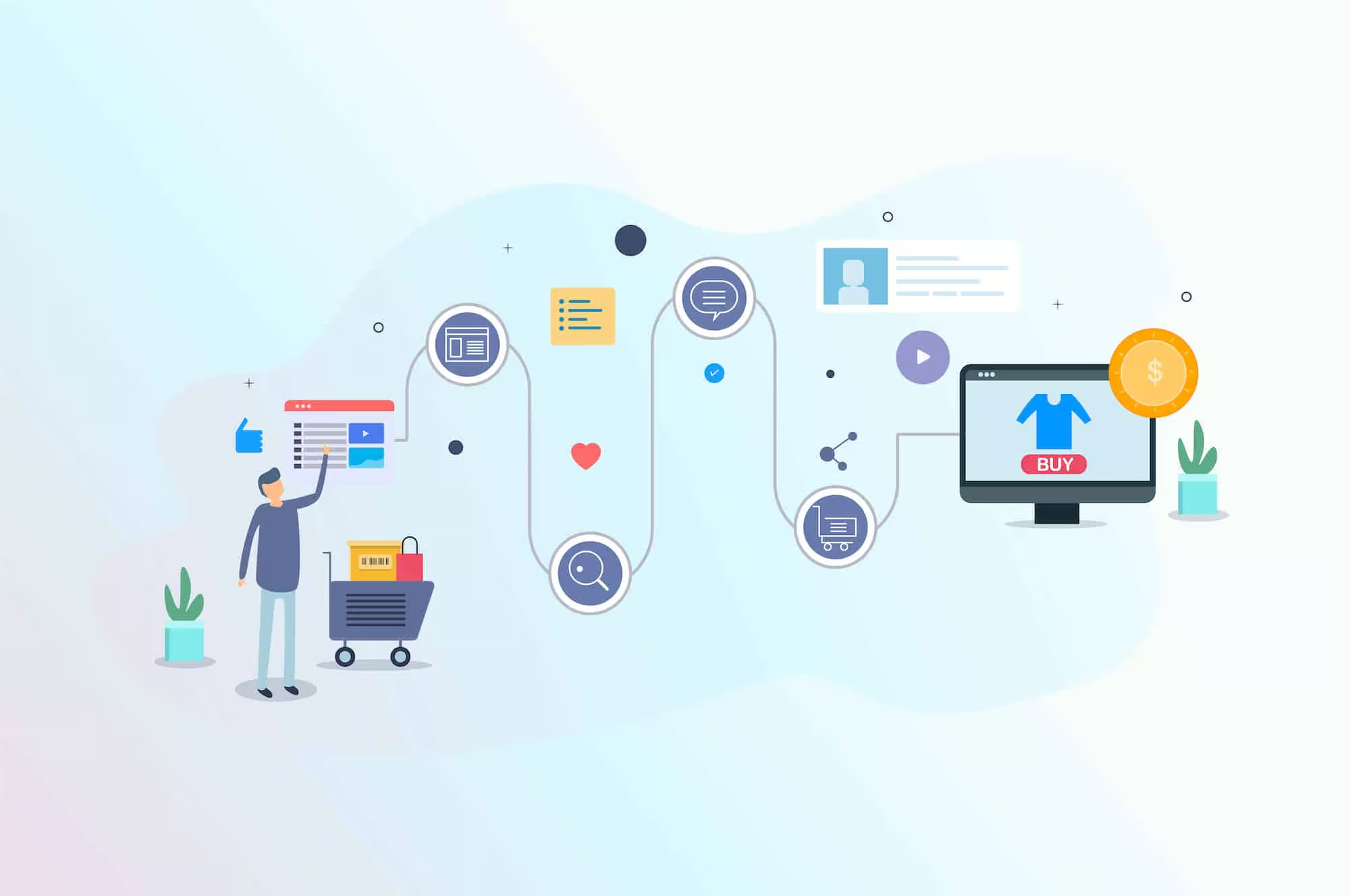
The User Journey
The design stage usually begins with outlining the paths (online and offline) a user will take that could impact their user experience. It is also crucial to look into the alternative paths they may take because things may not always happen how you want them to.
For example, you may have mapped out a path a user takes when he first enters your e-commerce website and to the product page but what happens when the product is out of stock? You do not want to lose your customers at this point of time so you may want to include a pop up that suggests them other similar products.
Therefore, it is important to always think of alternate paths your user will take when outlining their journey because all these little details affect their user experience!
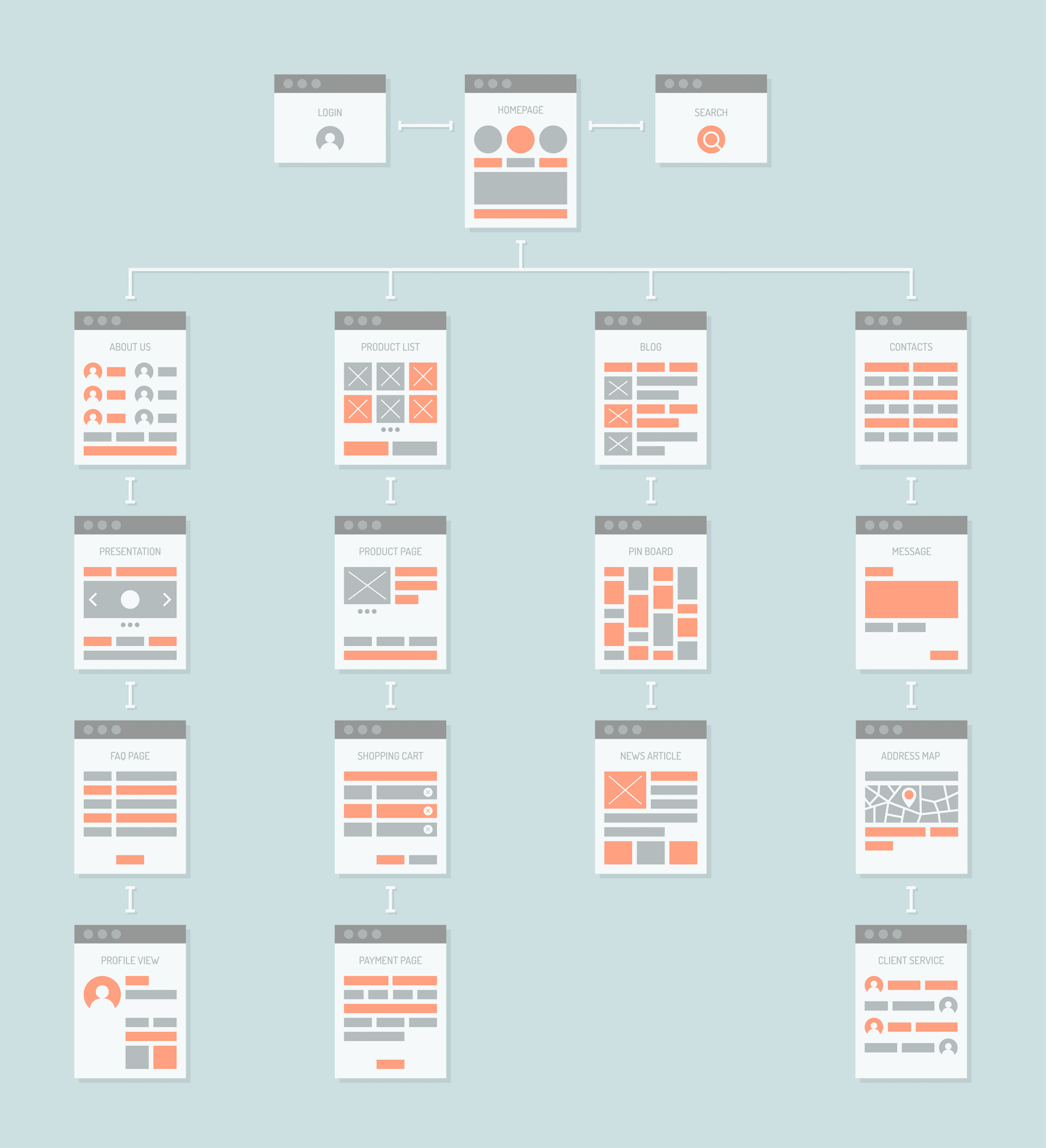
Information Architecture (IA)
IA is all about the organising and structuring of your website in a user-friendly and logical flow. It is built heavily on the user journeys you have defined. To make sure users a good user experience when navigating through your website, follow these 2 tips:
Organise your content
Organise the content in your drop-down menus. Your users should be able to easily find an option in the menu that allows them to find out more about the services you offer. Categorise your products if you are operating an e-commerce store. This will help users find what they want easily.
Use labels that your users will understand
Labels are words or icons that describe things. Find out what your users identify with, and be consistent and clear with it throughout your website.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Next, is to draw out wireframes. Wireframes are like blueprints. They are made up of lines and boxes linked together to show where things go on a website. Usually, UX designers use boxes to indicate where pictures, videos, texts and buttons should go on a wireframe. Wireframing can be done using pen and paper or using a wireframing software like Adobe XD.
When the UX designer is satisfied with the outline of the website, he will move into creating a prototype. Prototype is a sample version of your product e.g. a website. UX designers often use software such as Adobe XD to build an interactive prototype. This allows them to add actions to the design such that clicking on a button brings a user to another page.
This is extremely helpful as UX designers like doing user testing while creating their prototypes. In this way, potential users can play around with the prototype and give feedback on how it can be improved. Besides, it is also a great way to communicate the design to technical developers.
User Testing
User testing is something UX designers conduct either during or after prototyping. It allows people to mimic exactly what will happen on your website. It is important to carry out user testing because ultimately, the product (or website in this case) has to answer to your users’ needs and wants. User testing can also raise up things that are missing in the prototype.
From user testing, changes and improvements may be made depending on your project. After the final prototype is approved, UX designers will work closely with technical developers to bring the prototype to live.
Step 4 & 5: Develop and Release
In the developing stage, technical developers and UI designers will be working to develop the design UX designers have created from stage 1 – 3.
However, the job of a UX designer does not stop here. User testing is a continuous process even after the website is developed. It tests the reaction of people to your website design, and the insights gathered will be useful in helping you improve the user experience.
It is important to always remember to consider the experience of your user, design and make improvements based on their needs because UX design is all about helping people and solving problems!
Good User Experience (UX) Design Guidelines
A good UX design is always centred around the needs of your users, the usability and accessibility of it. To make sure the end product is usable, accessible and addresses the needs of users, I follow 4 basic and important guidelines when creating web designs.
#1: Simple and Intuitive
Users should be able to navigate easily through the design and “get it” immediately without any explanation and/or assistance. It should come naturally to them. Therefore, avoid any complexity in your design and organize according to a hierarchy to establish the importance level of each element.
#2: Engaging
Users should feel good and engaged when using your website. Your website should make them want to come back for more!
#3: Efficient
The fewer the clicks, the more efficient your design is. The design should be efficient with fewer clicks for users to complete tasks such as checking out their cart. Why let your users go through 6 clicks when he can just reach his destination with 3 clicks?
#4: Consistency
The overall look and feel should be consistent across all pages of the website. A few important things to look out for are your buttons, icons and font sizes. This makes each page familiar to your users and leave a good impression too.
What are some free courses I can go through for the basics of User Experience (UX) design?
Before getting into paid courses, I always try to find free ones. I am sure many of you are like me too! Here are the ones I have completed:
Beginner Course for UX Designers by Career Foundary
Digital Skills: User Experience by Accenture
Other than these 2 courses, UXBeginner.com also has a curated list of free UX design courses that you can check out!
Your Learning for User Experience (UX) Design Does Not Stop Here
A good UX designer does not stop after learning the fundamentals. It is imperative to master the basics but to improve your skills and become a better UX designer, you have to constantly read articles and watch videos from other UX designers in the field.
You can also subscribe to my newsletter to be updated when I publish UX related articles. Just like how the world is constantly evolving, UX design is the same too. There are so many useful tips emerging each day and one can never stop learning!
The Bottom Line
The most important thing you should remember is that UX design is centred around the needs of your users. It does not matter how nice your website looks when your users do not have a good experience while using it. As a UX designer, you always need to think in the shoes of your users.
Do you have a better understanding of the process of UX design now? Is there anything that I have missed out in this post? Let me know in the comments section below!